Audi Q7: Pressure Gauge, Tests and Measurements
General Information
Indicators on pressure gauge
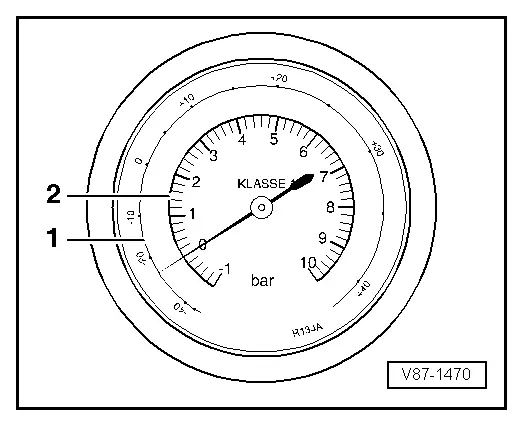
1 - Temperature scale for refrigerant R134a CF3-CH2F or CH2F-CF3.
2 - Pressure scale
 Note
Note
Pressure is measured in different units: 1 MPa (145 psi) corresponds to 10 bar (145 psi) positive pressure. 1 bar (14.5 psi) absolute pressure corresponds to 0 bar/psi positive pressure and thus to the ambient pressure (atmospheric pressure).
The pressure gauge may have one or more temperature scales next to the pressure scale. The R134a scale values are allocated respectively in the vapor pressure table. Since various refrigerants create different vapor pressures at the same temperature, each temperature scale is identified for the respective refrigerant.
Pressure Gauge Uses
Pressure and Temperature Measurement at Refrigerant Circuit
- High pressure gauge measures pressure and temperature, which expand uniformly from outlet of A/C compressor via the condenser up to constriction (restrictor, or expansion valve) with A/C system switched on.
- Low pressure gauge measures pressure and temperature, which expand uniformly from constriction (restrictor, or expansion valve) via evaporator up to input of A/C compressor with A/C system switched on.
 Note
Note
The relationship between pressure and temperature indicated on the gauges only exists in a refrigerant circuit that contains liquid or vapor, but not gas. In a gaseous state, the temperature is approximately 10 ºC to 30 ºC (50 ºF to 86 ºF) higher than indicated on the gauge.
Verification of Refrigerant in a Closed Container
Refrigerant R134a is present in a closed container or in a refrigerant circuit when temperature indicator on the pressure gauge matches the refrigerant temperature (standing fluid adopts the ambient temperature).
A closed container or a refrigerant circuit which has been switched off is empty when temperature indication on the pressure gauge is below the temperature of the refrigerant.
 Note
Note
The relationship between pressure and temperature indicated on the gauges no longer applies if no liquid is present and the pressure is built up solely by gas.
Service and Recycling Units
Extraction System Group Classifications
At this time, service units for extracting, cleaning and filling refrigerant for motor vehicle A/C systems are available on the market from various manufacturers.
Only certain service stations (with appropriate auxiliary device and different adapters if necessary) can be used for cleaning (flushing with refrigerant R134a) the refrigerant circuit. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a".
 WARNING
WARNING
When performing work on refrigerant circuit or when handling refrigerant observe all generally applicable safety precautions and pressure container regulations.
 Note
Note
- The service and recycling units used in motor vehicle workshops are extraction and charging systems not requiring a permit (Group "3") but which are only to be operated by qualified personnel. Instructions for unit operation and maintenance can be found in the relevant manufacturer's documentation.
- Extraction and charging systems of groups "1" and "2" are not used in motor vehicle workshops.
Extraction and charging systems of group "3":
Mobile extraction and charging systems for filling compressed-gas containers permanently connected to the system.
The refrigerant or refrigerant/oil mixture is transferred to compressed gas containers which are permanently connected to the mobile systems. In accordance with 3 Para. 5 No. 3 of pressure container regulations, compressed-gas containers are classified as pressure containers in this case.
The charging systems require:
- No permit
- no expert testing as the gas is transferred to compressed-gas containers which are classed as being pressure containers. (Systems used for transfer from these pressure containers to compressed-gas containers for supplying to third parties do however require a permit and are subject to mandatory testing).
Charging Systems not Requiring a Permit
At this time, service units for extracting, cleaning and filling refrigerant for motor vehicle A/C systems are available on the market from various manufacturers.
Only certain service stations (with appropriate auxiliary device and different adapters if necessary) can be used for cleaning (flushing with refrigerant R134a) the refrigerant circuit. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a".
 WARNING
WARNING
When performing work on refrigerant circuit or when handling refrigerant observe all generally applicable safety precautions and pressure container regulations.
Charging systems not requiring a permit are ones used for transferring compressed gases to mobile compressed-gas containers for internal use only.
Note:
Some service units are charging systems not requiring a permit. When working with such equipment, the refrigerant is not transferred to mobile compressed-gas containers, but rather into a permanently installed charging cylinder with visible level gauge and float switch.
Recommendation:
It is advisable to use a portable cylinder with visible level gauge and pressure relief valve for surplus refrigerant for internal use.
Attention must be paid to technical regulations for compressed gases (for example TRGS 400, TRGS 402, TRGS 407 TRGS 510 TRGS 725/TRBS3145) when transferring compressed gases to other compressed-gas containers.
Refrigerant Circuit Repair Information
 WARNING
WARNING
When performing work on refrigerant circuit, observe all generally applicable safety precautions and pressure container regulations.
Special Tools and Accessories:
The performance of proper workmanlike repairs on an air conditioning system:
- Requires the use of special tools and materials as listed. Refer to → Chapter "Tools and Equipment".
- Requires compliance with the basic instructions for use of leak detectors. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Determining Leaks ".
- Requires expert knowledge.
 Note
Note
Environmentally hazardous draining of refrigerant is an offense punishable by law. For laws and regulations. Refer to → Chapter "Laws and Regulations".