Audi Q7: Refrigerant Circuit Pressures Specified Values, Vehicles with Heat Pump
 Note
Note
- On vehicles with a high-voltage system and heat pump (for example on the Audi Q7 e-tron) installed in the refrigerant circuit and electrically activated vehicles which regulate the flow of the refrigerant in the refrigerant circuit depending on the current operating condition. There are different versions of these valves. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit and use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function.
- On vehicles with the "heat pump" function and/or "high-voltage battery cooling" in not all operating conditions is the A/C system high pressure on the service connection of the high pressure side. The refrigerant circuit pressure on the high pressure side can on these vehicles depending on the operating conditions of the A/C system, can only be measured via the pressure/temperature sensor installed in the refrigerant circuit. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit and the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function.
- On these vehicles the refrigerant circuit of the A/C system is used not only to cool the vehicle interior but also to cool the Hybrid Battery Unit -AX1- (via the refrigerant circuit for the high-voltage system) and to heat the vehicle interior (at low ambient temperature) via the heat pump function. So that this function can be driven the different valves pressure and temperature sensors as well as the pumps in the refrigerant circuit and in the refrigerant circuit of the high-voltage system must be installed correctly and function correctly. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit, use the → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and → Engine Mechanical; Rep. Gr.19; Cooling System/Coolant; Coolant, Draining and Filling.
- To determine the possible cause of a malfunction, the basic setting of the Thermal Management Control Module -J1024- different routines are stored, which activate these functions "Cooling the A/C system", "heat pump", and "Cooling the components of the high-voltage system" in the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester"Guided Fault Finding" function.
High-pressure side:
Increasing from initial pressure (when connecting the pressure gauges) to a maximum of 20 bar.
 Note
Note
Depending on the layout of the high pressure side service connection and the operating condition the high pressure side can only be measured via the pressure/temperature sensor installed in the refrigerant circuit. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit.
Low-pressure side:
Decreasing from initial pressure (when connecting the pressure gauges) to a value between 1.5 and 2.3 bar absolute pressure (depending on the required cooling output).
A/C compressor speed:
Depending on the required cooling output between 800 and 8600/min (currently a maximum of 5000/min for parked vehicles).
 Note
Note
- The temperature of the air after the evaporator, the current A/C compressor speed and the pressure of the refrigerant on the high pressure side, are displayed as the measured value depending on the vehicle of the different control modules (for example from the Thermal Management Control Module -J1024-, from the Front A/C Display Control Head -E87- or from the Climatronic Control Module -J255-). Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit, use the → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function.
- If a high cooling output is required (for example, a high outside temperature and the blower speed set on high), then the A/C compressor will not bring the pressure on the low pressure side to the required value (for example, for a certain time after turning on the A/C). The A/C compressor is not actuated at the maximum specified speed (of approximately 8500/min) on a stationary or slow moving vehicle (up to a speed of approximately 45km/h) (the A/C compressor speed is limited to approximately 5000/min). After a vehicle reaches a speed of more than approximately 45 km/h, the limit for the maximum permissible A/C compressor speed is lifted. At a A/C compressor speed of 5000/min, a high outside temperature and a high fresh air blower speed (inefficient environmental controls), the A/C compressor output (the delivery volume) is no longer sufficient to reduce the pressure on the low pressure side to the target value. To check the A/C compressor control under these conditions, for example, the fresh air blower is controlled only with approximately 40% of the maximum voltage, check the pressures at a lower fresh air blower speed. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function for A/C system and the battery regulation and the → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.00; Repair Instructions; Checking Cooling Output.
- Under unfavorable conditions (very high ambient temperatures, high humidity), pressure on high-pressure side may increase to max. 29 bar.
- The specified speed of the A/C compressor is displayed and the measured value for example from the Thermal Management Control Module -J1024- using the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function.
- The refrigerant circuit pressure (low or high pressure) measured from the different pressure/temperature sensors depending on the respective operating condition is displayed as the measured value from the respective control module. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit.
- The low pressure settles depending on the A/C compressor speed and the control characteristic of the expansion valve (on the evaporator of the front heater and A/C unit) within the compressor output range in tolerance range (1.5 to 2.3 bar positive pressure).
- The target speed for the A/C compressor must be greater than 1500/min for this test.
- In setting "maximum cooling output" the target speed is regulated to approximately 4000 up to 5000/min. This value is vehicle-specific and is displayed and the measured value of the respective control module using the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function.
- At absolute pressure, 0 bar corresponds to absolute vacuum. Normal ambient pressure corresponds to 1 bar absolute pressure. 0 bar pressure corresponds to an absolute pressure of 1 bar on most pressure gauges (indicated by -1 bar below 0).
- If on a vehicle with two evaporators (one in the heater and A/C unit and one for cooling the heater and A/C unit for example the heat exchanger for the high-voltage battery) and two condensers (one in the front end for the A/C system and one as the heat exchanger for the heat pump function) depending on the selected function on a component the measured temperature or pressure, the specified value corresponds to another component whose specifications are not achieved, check the activation of the electrically activated valves installed in the refrigerant circuit. At the same time pay attention to the pressure distribution in the refrigerant circuit depending on the installed check valves use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function are refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit.
- For the correct A/C function it is also necessary that depending on the selected functions of the respective heater cores enough heat is supplied or removed. Pay attention for this reason to the incorporation of the heater core in the respective engine coolant circuit and the high-voltage system and the function of the pumps and valves installed in it. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Coolant Circuit.
- Since the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage components output (in the battery cooling module and in the high-voltage battery heat exchanger) is smaller than the evaporator output in the heater and A/C unit, the required target temperature may still be reached in the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage battery with too little refrigerant in the refrigerant circuit, but the target temperature in the heater and A/C unit evaporator will no longer be attainable (even though the A/C compressor is activated with increased A/C unit speed).
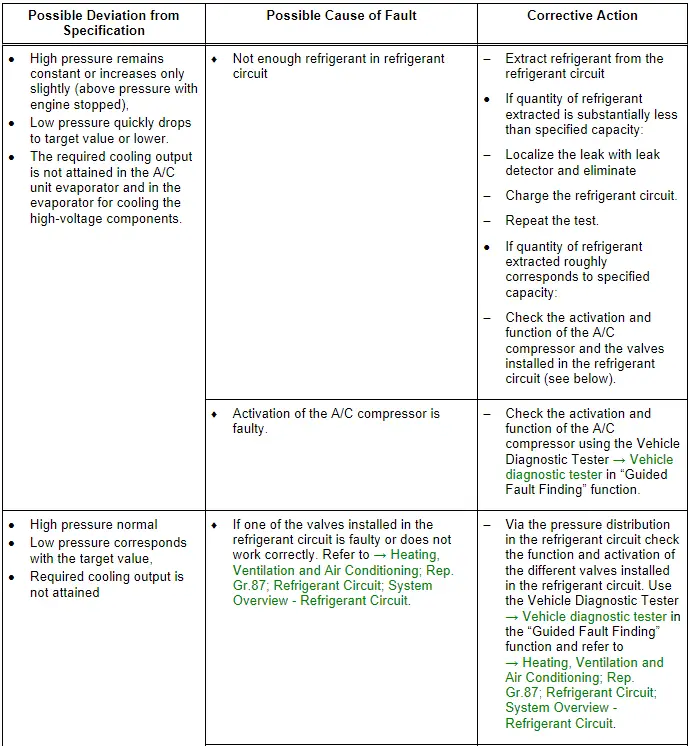

 Note
Note
- To determine the possible cause of a malfunction, the basic setting of the respective control module (for example in the Thermal Management Control Module -J1024-) different routines are stored, which activate these functions "Cooling the A/C system", "heat pump", and "Cooling the components of the high-voltage system" in the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester"Guided Fault Finding" function.
- If for this concern no malfunction can be determined, check the activation of the electrically activated valves installed in the refrigerant circuit next. A malfunction can be determined here by removing and checking the check valves installed in the refrigerant circuit, if no malfunction can be determined here clean the refrigerant circuit (flush with refrigerant R134a, a constriction or a blockage in the refrigerant circuit can also lead to these complaints. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit and → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a".
- On vehicles with the "heat pump" function and/or "high-voltage battery cooling" in not all operating conditions is the A/C system high pressure on the service connection of the high pressure side. The refrigerant circuit pressure on the high pressure side can on these vehicles depending on the operating conditions of the A/C system, can only be measured via the pressure/temperature sensor installed in the refrigerant circuit. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit and the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function.
- Before beginning the repair work check the measured values of the different pressure/temperature sensors installed in the refrigerant circuit. If there is a malfunction in the measured value of a pressure/temperature sensor tis can lead to problems in the cooling output or the freezing-up of the evaporator in the front heater and A/C unit. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Refrigerant Circuit; System Overview - Refrigerant Circuit, use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Wiring diagrams, Troubleshooting & Component locations.
- Pay attention when checking the different functions (heat pump or cooling the high-voltage battery) and the activation and function of the refrigerant circuit components when are in connection with these functions. Refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Coolant Circuit.
- If the A/C system function is not OK after repeating the test, for example after replacing expansion valve (reinstalling the old expansion valve), clean the refrigerant circuit by flushing using the refrigerant R134a. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a". Then replace the A/C compressor and receiver/dryer or dryer cartridge.
- With a malfunction on one of the temperature sensors, the evaporator may ice up even though the quantity of refrigerant in the circuit is OK.
- If the expansion valve in the A/C unit evaporator or the heater and A/C unit is malfunctioning (permanently closed or does not open sufficiently), the A/C compressor is actuated to maximum output and the low pressure drops to value in graph or below (compressor draws off refrigerant from low-pressure side). Since the refrigerant cannot flow via the expansion valve, the cooling output is not attained, high pressure may also not increase or only increase slightly due to the absence of energy. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.00 ; Repair Instructions; Checking Cooling Output (vehicle-specific repair manual).
- The evaporator in the heater and A/C unit has a larger output than the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage battery. The expansion valve in front of this evaporator (the heat exchanger for the cooling of the components of the high-voltage system) is activated depending on the version to cool the Electric Vehicle Battery - A2-/Hybrid Battery Unit -AX1- (Hybrid battery) first from or through a specified battery temperature from the respective control module, so that the absence of energy via this evaporator is not or only slightly raised. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.00; Repair Instructions; Checking Cooling Output.
- If there is too much refrigerant oil in the circuit, the compressor must be drained (flushed) and the receiver/dryer or dryer cartridge must be replaced. After cleaning the refrigerant circuit by flushing with refrigerant R134a. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a". Fill the refrigerant circuit with the correct quantity of refrigerant (in the A/C compressor). Refer to → Chapter "Approved Refrigerant Oils and Capacities".
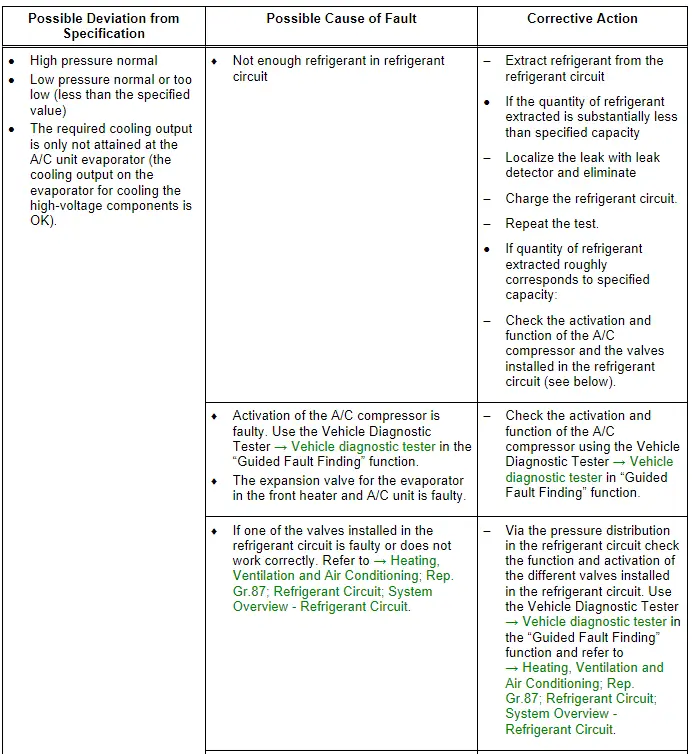

 Note
Note
Read the supporting information.
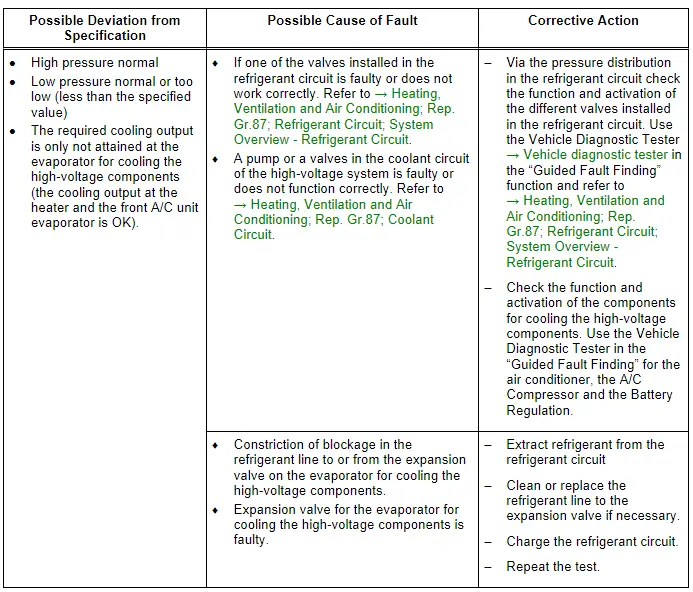
 Note
Note
Read the supporting information.
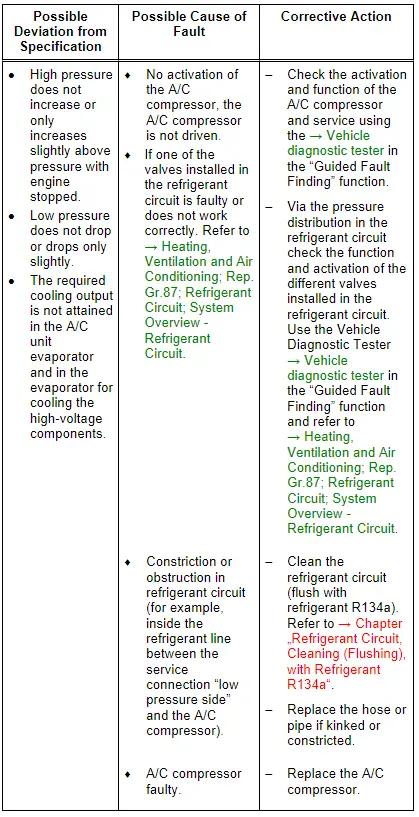
 Note
Note
Read the supporting information.
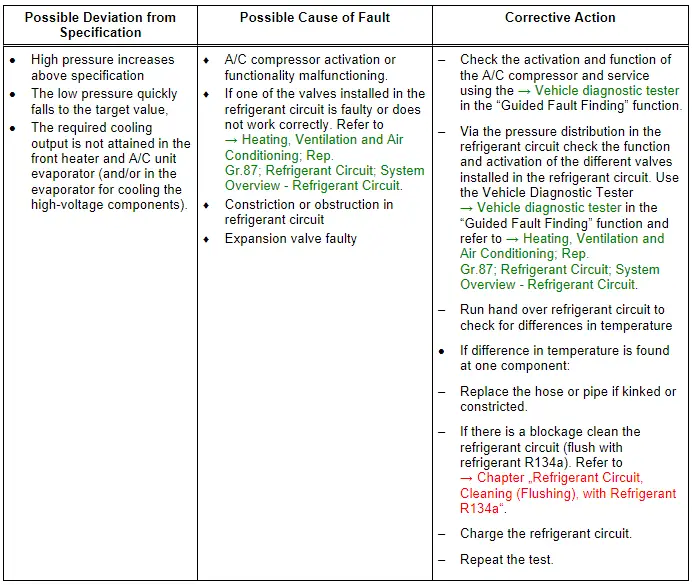
 Note
Note
- With this malfunction, evaporator may ice up although the quantity of refrigerant in circuit is OK.
- If the expansion valve in the heater and A/C unit evaporator or the installed shut-off valve is malfunctioning (permanently closed or does not open sufficiently), the A/C compressor is actuated to maximum output and the low pressure drops to specification or below (compressor draws off refrigerant from low-pressure side). Since no (or little) the refrigerant can flow via the expansion valve, the cooling output is not attained, high pressure may also not increase or only increase slightly due to the absence of energy. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.00 ; Repair Instructions; Checking Cooling Output (vehicle-specific repair manual).
- If the expansion valve for the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage components is faulty (or the function and activation is faulty) is always closed or does not open wide enough the A/C compressor is also activated with the maximum output (the required temperatures in the heat exchanger are not reached). The pressure on the low pressure side only then falls to the specified value or lower when at the same time the front heater and A/C unit no cooling output is needed. The A/C compressor extracts the refrigerant from the low pressure side from both evaporators. Because no refrigerant can low over the expansion valve in the front heater and A/C unit and the cooling output in the evaporator for cooling the high voltage battery is not reached (there is a malfunction in the area of the evaporator for the cooling of the high voltage battery) the electric A/C compressor is activated with a higher speed. If not refrigerant can flow the pressure on the low pressure side falls under the specified value, high pressure may also not increase or only increase slightly due to the absence of energy. The same applies if a valve in the refrigerant circuit is not OK a malfunction in the incorporation of the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage battery in the high-voltage system refrigerant circuit or the pump or a valve installed there is not OK. Then the high-Voltage Battery Heat Exchanger is cooled, but the cooled coolant reached the high-voltage battery heat exchanger which should not be cooled. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Coolant Circuit (vehicle-specific repair manual).
- For additional information.
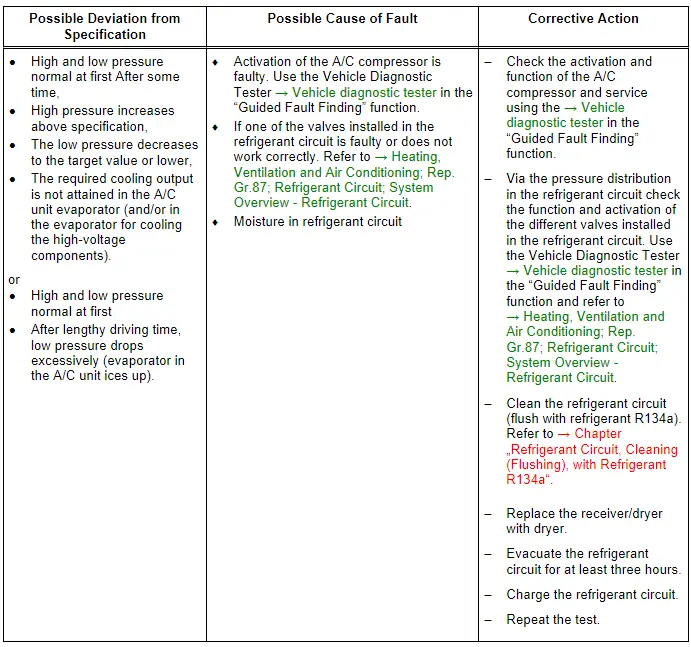
 Note
Note
- First, it is not necessary to clean the refrigerant circuit (flushing with refrigerant R134a, refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a") in case of this complaint because generally only a small amount of moisture is in the system and this can be removed by a long evacuation.
- If a problem involving moisture in refrigerant circuit only occurs after a lengthy operating period or only infrequently (low pressure drops below specification and evaporator ices up), it is sufficient to replace the dryer installed in receiver/dryer (adjust quantity of refrigerant oil). Refrigerant circuit is then to be evacuated for at least three hours.
- With this malfunction, evaporator may ice up although the quantity of refrigerant in circuit is OK.
- A malfunction on the Evaporator Vent Temperature Sensor -G263- or/and on the pressure/temperature sensor the can lead to the refrigerant circuit freezing-up. For this concern also pay attention to the measured values of the different pressure/temperature sensor in the refrigerant circuit. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.00; Repair Instructions; Checking Cooling Output (vehicle-specific repair manual).
- For additional information.
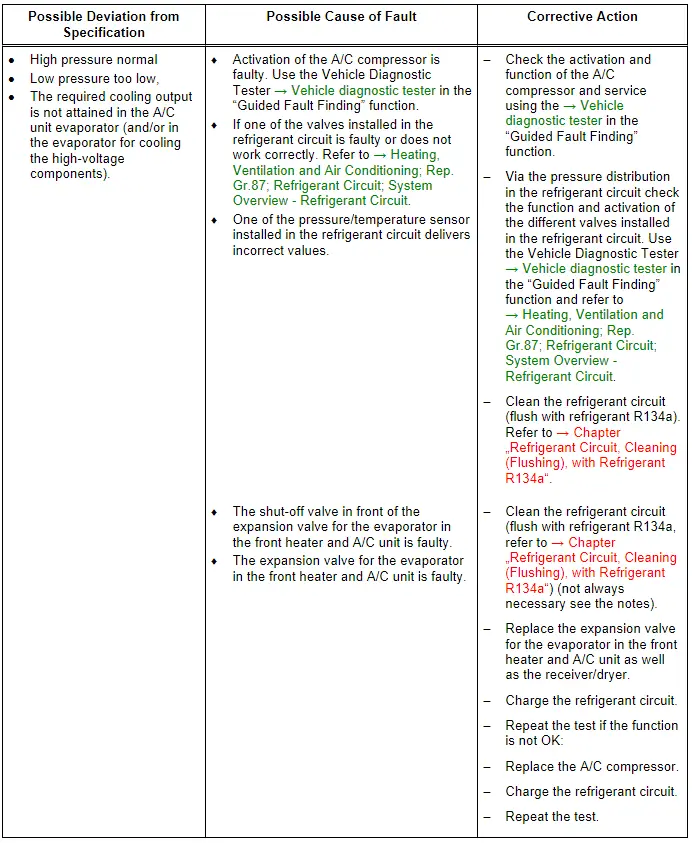
 Note
Note
- For the malfunction "high pressure normal, low pressure too low", note the following: With this fault, it may be that the evaporator in the A/C unit is icing up although the refrigerant quantity in the circuit is OK.
- If there is a fault in the A/C compressor (the A/C compressor is activated by the A/C Compressor Control Module -J842- at too high of a speed), it is not necessary to clean the refrigerant circuit by flushing with refrigerant R134a. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a". In this case, it is sufficient to replace the A/C compressor (observe quantity of refrigerant oil in A/C compressor and if necessary adjust).
- If the expansion valve for the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage components is faulty (or the function and activation is faulty) is always closed or does not open wide enough the A/C compressor is also activated with the maximum output (the required temperatures in the heat exchanger are not reached). The pressure on the low pressure side only then falls to the specified value or lower when at the same time the front heater and A/C unit no cooling output is needed. The A/C compressor extracts the refrigerant from the low pressure side from both evaporators. Because no refrigerant can low over the expansion valve in the front heater and A/C unit and the cooling output in the evaporator for cooling the high voltage battery is not reached (there is a malfunction in the area of the evaporator for the cooling of the high voltage battery) the electric A/C compressor is activated with a higher speed. If not refrigerant can flow the pressure on the low pressure side falls under the specified value, high pressure may also not increase or only increase slightly due to the absence of energy. The same applies if a valve in the refrigerant circuit is not OK a malfunction in the incorporation of the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage battery in the high-voltage system refrigerant circuit or the pump or a valve installed there is not OK. Then the high-Voltage Battery Heat Exchanger is cooled, but the cooled coolant reached the high-voltage battery heat exchanger which should not be cooled. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Coolant Circuit (vehicle-specific repair manual).
- A malfunction on the Evaporator Vent Temperature Sensor -G263- or/and on the pressure/temperature sensor the can lead to this concern. Also pay attention to the measured values of the different pressure/temperature sensor in the refrigerant circuit. Use the → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.00; Repair Instructions; Checking Cooling Output (vehicle-specific repair manual).
- For additional information.
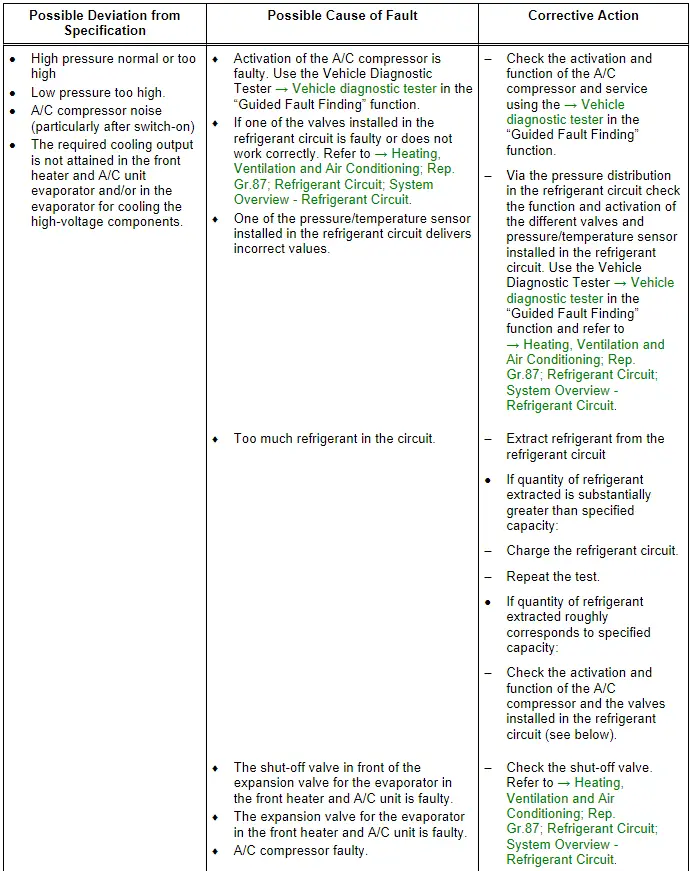

 Note
Note
- This fault may also be caused by too much refrigerant oil in the circuit. Overfilling with refrigerant oil can occur if, for example, the compressor has been replaced without adjusting the quantity of refrigerant oil.
- For additional information.
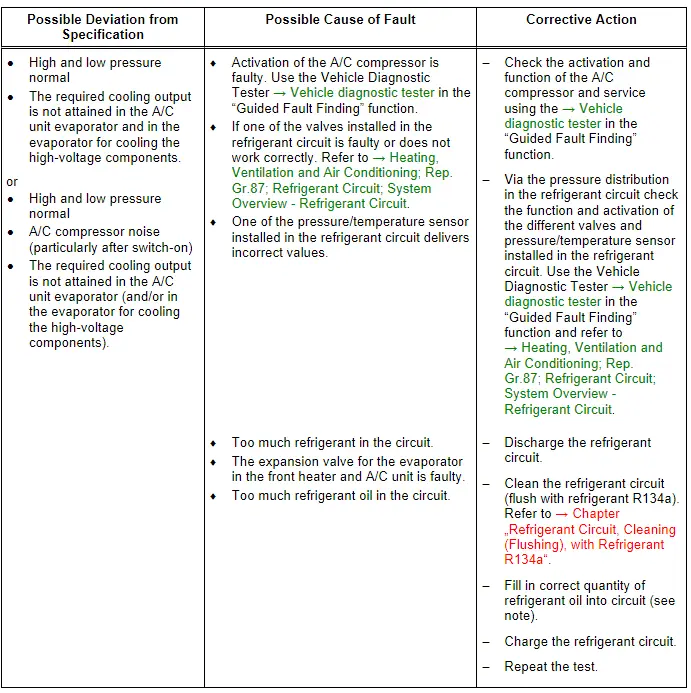
 Note
Note
- Overfilling with refrigerant oil can occur if, for example, the compressor has been replaced without adjusting the quantity of refrigerant oil.
- If for example the expansion valve for the evaporator in the A/C unit or for the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage battery is faulty (always open) the evaporator temperature (in the heater and A/C unit) is no longer regulated that only refrigerant in gaseous state exits from the evaporator. Under certain usage conditions, liquid droplets may then be drawn in by the compressor and cause noise (liquid cannot be compressed).
- If there is too much refrigerant oil in the circuit, the compressor must be drained and the receiver/dryer must be replaced. After cleaning the refrigerant circuit by flushing with refrigerant R134a. Refer to → Chapter "Refrigerant Circuit, Cleaning (Flushing), with Refrigerant R134a". Fill the refrigerant circuit with the correct quantity of refrigerant. Refer to → Chapter "Approved Refrigerant Oils and Capacities".
- For additional information.
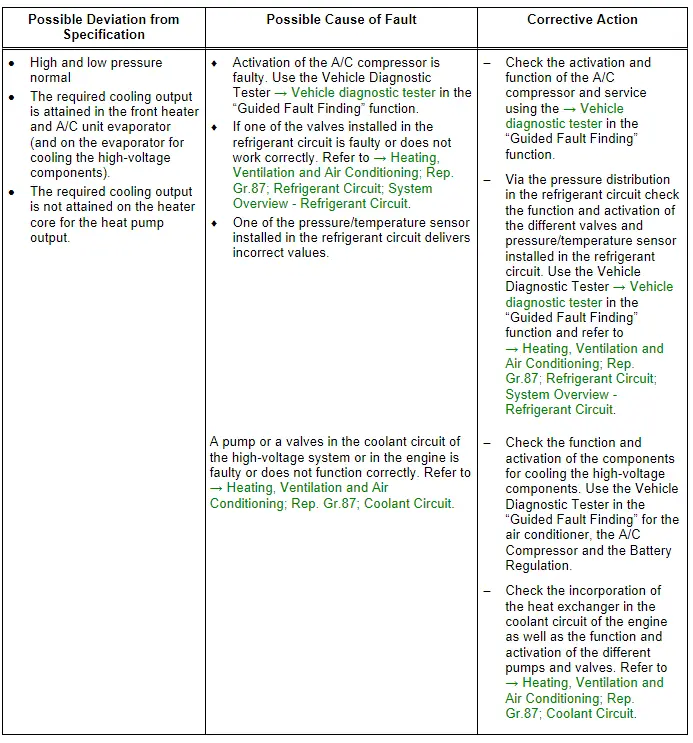
 Note
Note
- If the required cooling output on the evaporator in the front heater and A/C unit (and on the evaporator for cooling the high-voltage battery is OK) and there is a concern due to insufficient heating performance on the heat exchanger for the heat pump operation. The cause may be in the high-voltage system coolant circuit or in the engine coolant circuit. If the pumps and valves in the high-voltage system coolant circuit is not activated correctly or its function is not OK via the evaporator (heat exchanger) for the high-voltage system components not enough heat energy is absorbed from the coolant. If the pumps and valves in the coolant circuit of the engine are not started correctly or its function are not OK via the heat exchanger for the heat pump function for absorbing the heat energy is not transferred to the coolant flowing to the heat exchanger in the heater and A/C unit. Use the Vehicle Diagnostic Tester → Vehicle diagnostic tester in the "Guided Fault Finding" function and refer to → Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning; Rep. Gr.87; Coolant Circuit (vehicle-specific repair manual).
- For additional information.

